Thermoset Molding for High Heat Components
There are two main types of plastics: Thermoplastic and thermoset. Thermoplastic materials are more common molding materials such as nylon, ABS, polypropylene, and polycarbonate, among others. These thermoplastics are generally used in more price-sensitive components that do not require improved material performance properties. Thermoset plastics on the other hand are heat-stable materials suitable for components that operate in aggressive environments including high temperatures, outdoor, electrical applications. Utilizing a thermoset material within a molded product gives the end part stability in such elements, allowing the product assembly to remain durable over the life of the product and ensure its safety during operating use. Compared to thermosets, many thermoplastics will degrade in high temperatures or outdoor environments, jeopardizing the integrity of the product assembly and internal components.
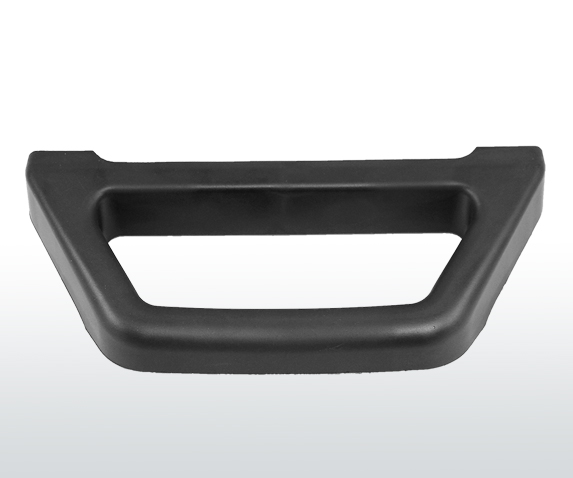
Most thermoset formulations offer temperature deflection properties up to 400-500° Fahrenheit, with applicable UL yellowcard flammability ratings of V0 and 5VA. Applications such as electrical housings, covers, and bases are molded from thermosets, providing electrical insulation to protect internal components and wiring from overheating and potential product failure or fire. Automotive components used in powertrain and transmission applications rely on thermosets for its chemical resistance properties, allowing molded thermosets operating in oils and automotive fluids to remain structurally and chemically stable. In the appliance industry, consumer appliances incorporate molded thermosets for handles, knobs, faceplates, side walls, and bases for both performance and aesthetic benefits where components need to remain durable in high temperatures, yet offer a great aesthetic to consumers.




Comments are closed